

|
|
Integrate liquid lenses into imaging assemblies for quick autofocus |
|
|
Compensate for different object sizes and working distances |
|
|
Increase throughput in high-speed machine vision systems |
|
|
Ideal for barcode reading, rapid automation, package sorting, and security |
Conventional imaging lenses struggle to capture sharp and accurate images in high-speed or precise applications that require quick refocusing. Liquid lenses overcome these limitations by quickly adjusting focus to accommodate for objects located at various working distances or objects of different heights. Liquid lenses are small cells containing optical-grade liquid that change their shape when a current or voltage is applied. This occurs within a matter of milliseconds and causes the lens’ optical power, and therefore focal length and working distance, to shift. Integrating liquid lenses into imaging systems is an ideal solution for applications requiring rapid focusing, high throughput, and accommodation for depth of field and working distance.
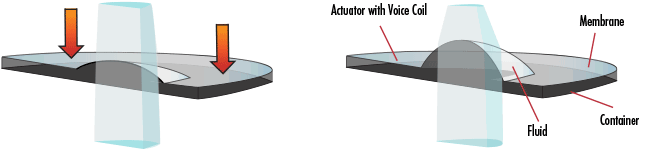
Liquid lenses can function by several slightly different processes: electrowetting, current-driven polymers, or sound piezoelectrics. Electrically-focused liquid lenses consist of a container filled with optical fluid and a surrounding polymer membrane. A current-driven actuator applies pressure to the edges of the membrane, causing the curvature of the lens (and therefore its optical power) to change. Electrically-focused tunable lenses focus within milliseconds and function with low operating voltages. They do not alter polarization, typically have high laser damage thresholds, and introduce minimal aberrations.
The video below shows a demonstration of how liquid lens technology can be used to inspect objects of different heights.
To learn more about liquid lens applications, features, and technologies, please read our application note.
 How quickly can liquid lenses change between different focus positions?
How quickly can liquid lenses change between different focus positions?
 What aperture sizes are available in liquid lenses from Edmund Optics®?
What aperture sizes are available in liquid lenses from Edmund Optics®?
Variable Focus Liquid Lenses come in aperture sizes ranging from 2.5-3.9mm and Optotune Electrically Focus-Tunable Lenses come in aperture sizes ranging from 3-26mm.
 Can I integrate a liquid lens into another type of lens, such as a fixed focal length lens?
Can I integrate a liquid lens into another type of lens, such as a fixed focal length lens?
Yes, we can integrate liquid lenses into other types of lenses as a custom request. We also offer the modular Cx Series Fixed Focal Length Lenses, in which you can integrate interchangeable accessories including liquid lenses, fixed apertures, and internal filter holders.
 How do I use a C-Mount Focus Tunable Lens in combination with a fixed focal length lens assembly?
How do I use a C-Mount Focus Tunable Lens in combination with a fixed focal length lens assembly?
A thread adapter can be used to connect a C-Mount Focus Tunable Lens directly onto the filter threads of a fixed focal length lens assembly. To learn more, visit our Using C-Mount Focus Tunable Lenses application note.
or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2023 | Edmund Optics, Ltd Unit 1, Opus Avenue, Nether Poppleton, York, YO26 6BL, UK
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act